Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Association of Shift Work with Normal-Weight Obesity in Community-Dwelling Adults
- Chul Woo Ahn, Sungjae Shin, Seunghyun Lee, Hye-Sun Park, Namki Hong, Yumie Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(5):781-790. Published online October 25, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1532
- 3,270 View
- 189 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Shift work is associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome. However, this association in the normal-weight population remains unclear. This study aimed to investigate whether shift work is associated with normal-weight obesity (NWO).
Methods
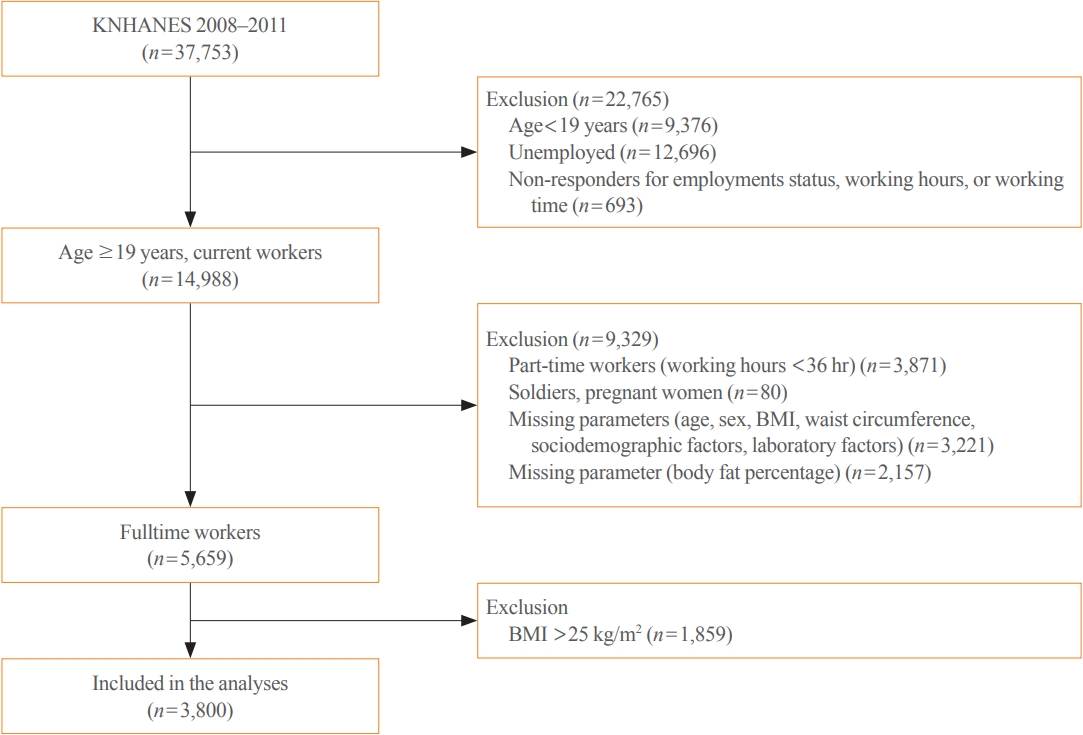
From the nationally representative Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) dataset (2008 to 2011), 3,800 full-time workers aged ≥19 years with a body mass index (BMI) ≤25 kg/m2 were analysed. We defined NWO as BMI ≤25 kg/m2 and body fat percentage ≥25% in men and ≥37% in women. Working patterns were classified into “daytime,” “other than daytime,” and “shift.” Multivariable logistic regression analysis was performed to evaluate the relationship between shift work and NWO.
Results
Shift work was associated with higher odds of NWO than daytime work (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.47; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.04 to 2.09) and night/evening work (aOR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.11 to 3.14) after adjustment for type of work, working hours, age, sex, BMI, 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels, homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance, and other sociodemographic factors. In subgroup analyses, the association between shift work and NWO was more robust in those aged ≥60 years and those working ≥56 hours/week.
Conclusion
Shift work was associated with NWO in community-dwelling Korean adults, independent of age, sex, BMI, and other covariates. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impaired Melatonin Secretion, Oxidative Stress and Metabolic Syndrome in Night Shift Work
Sorina Hohor, Cristina Mandanach, Andreea Maftei, Corina Aurelia Zugravu, Marina Ruxandra Oțelea
Antioxidants.2023; 12(4): 959. CrossRef - Normal-Weight Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults: A Population-Based Cross-Sectional Study
Jeonghyeon Kim, Seamon Kang, Hyunsik Kang
Healthcare.2023; 11(16): 2303. CrossRef - You Can’t Avoid Shift Work? Then Focus on Body Fat Rather than Weight
Eun Kyung Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(5): 756. CrossRef
- Impaired Melatonin Secretion, Oxidative Stress and Metabolic Syndrome in Night Shift Work

- Clinical Study
- Current Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Primary Care Clinics in Korea
- Da Hea Seo, Shinae Kang, Yong-ho Lee, Jung Yoon Ha, Jong Suk Park, Byoung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Chul Woo Ahn, Bong-Soo Cha
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(3):282-290. Published online September 26, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.3.282
- 5,992 View
- 87 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background This study investigated the overall status of diabetes control and screening for diabetic microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus attending primary care clinics in Korea.
Methods In this cross-sectional observational study, 191 primary care clinics were randomly selected across Korea from 2015 to 2016. In total, 3,227 subjects were enrolled in the study.
Results The patients followed at the primary care clinics were relatively young, with a mean age of 61.4±11.7 years, and had a relatively short duration of diabetes (mean duration, 7.6±6.5 years). Approximately 14% of subjects had diabetic microvascular complications. However, the patients treated at the primary care clinics had suboptimal control of hemoglobin A1c levels, blood pressure, and serum lipid levels, along with a metabolic target achievement rate of 5.9% according to the Korean Diabetes Association guidelines. The screening rates for diabetic nephropathy, retinopathy, and neuropathy within the past 12 months were 28.4%, 23.3%, and 13.3%, respectively.
Conclusion The overall status of diabetes management, including the frequency of screening for microvascular complications, was suboptimal in the primary care clinics. More efforts should be made and more resources need to be allocated for primary care physicians to promote adequate healthcare delivery, which would result in stricter diabetes control and improved management of diabetic complications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 525. CrossRef - Comparison of on-Statin Lipid and Lipoprotein Levels for the Prediction of First Cardiovascular Event in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ji Yoon Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 837. CrossRef - Effectiveness of quality of care for patients with type 2 diabetes in China: findings from the Shanghai Integration Model (SIM)
Chun Cai, Yuexing Liu, Yanyun Li, Yan Shi, Haidong Zou, Yuqian Bao, Yun Shen, Xin Cui, Chen Fu, Weiping Jia
Frontiers of Medicine.2022; 16(1): 126. CrossRef - Comparison of Health Outcomes by Care Provider Type for Newly Diagnosed Mild Type 2 Diabetes Patients in South Korea: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Hee-Chung Kang, Jae-Seok Hong
Healthcare.2022; 10(2): 334. CrossRef - Management Status of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at General Hospitals in Korea: A 5-Year Follow-Up Study
Jin Hee Jung, Jung Hwa Lee, Hyang Mi Jang, Young Na, Hee Sun Choi, Yeon Hee Lee, Yang Gyo Kang, Na Rae Kim, Jeong Rim Lee, Bok Rye Song, Kang Hee Sim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(1): 64. CrossRef - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Early Dry Skin Disorder: A Comparison Study Between Primary and Tertiary Care in Indonesia
Lili Legiawati, Kusmarinah Bramono, Wresti Indriatmi, Em Yunir, Aditya Indra Pratama
Current Diabetes Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-Term Changes in HbA1c According to Blood Glucose Control Status During the First 3 Months After Visiting a Tertiary University Hospital
Hyunah Kim, Da Young Jung, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Hyeon Woo Yim, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Differences in health behavior and nutrient intake status between diabetes-aware and unaware Korean adults based on the Korea national health and nutrition examination survey 2016–18 data: A cross-sectional study
Anshul Sharma, Chen Lulu, Kee-Ho Song, Hae-Jeung Lee
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Diabetes Quality Assessment on Diabetes Management Behaviors Based on a Nationwide Survey
Chang Kyun Choi, Jungho Yang, Ji-An Jeong, Min-Ho Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(23): 15781. CrossRef - The Impact of the Indonesian Chronic Disease Management Program (PROLANIS) on Metabolic Control and Renal Function of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in Primary Care Setting
Firas Farisi Alkaff, Fauzan Illavi, Sovia Salamah, Wiwit Setiyawati, Ristra Ramadhani, Elly Purwantini, Dicky L. Tahapary
Journal of Primary Care & Community Health.2021; 12: 215013272098440. CrossRef - Questionnaire-based Survey of Demographic and Clinical Characteristics, Health Behaviors, and Mental Health of Young Korean Adults with Early-Onset Diabetes
Ji In Park, Hyunjeong Baek, Sang-Wook Kim, Ji Yun Jeong, Kee-Ho Song, Ji Hee Yu, Il Sung Nam-Goong, Eun-Hee Cho
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors and Risk of Retinal Vein Occlusion Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Propensity Score–Matched Cohort Study
Min-Kyung Lee, Bongsung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Hyuk Lee, Minhee Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Young-Jung Roh
Diabetes Care.2021; 44(10): 2419. CrossRef - Challenges in the Management of Diabetes in Primary Care
Yeon Kyung Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(3): 161. CrossRef - Does Diabetes Increase the Risk of Contracting COVID-19? A Population-Based Study in Korea
Sung-Youn Chun, Dong Wook Kim, Sang Ah Lee, Su Jung Lee, Jung Hyun Chang, Yoon Jung Choi, Seong Woo Kim, Sun Ok Song
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 897. CrossRef - Comprehensive Efforts Are Needed to Improve the Quality of Primary Diabetes Care in Korea
Chan-Hee Jung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(3): 265. CrossRef
- Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study

- Clinical Study
- Triglyceride Glucose Index Is Superior to the Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance for Predicting Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Korean Adults
- Sang Bae Lee, Min Kyung Kim, Shinae Kang, Kahui Park, Jung Hye Kim, Su Jung Baik, Ji Sun Nam, Chul Woo Ahn, Jong Suk Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(2):179-186. Published online May 20, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.2.179
- 7,370 View
- 143 Download
- 81 Web of Science
- 80 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Recently, the triglyceride glucose (TyG) index has been considered a surrogate marker of insulin resistance which is a well-known pathogenic factor in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). However, few studies have investigated the relationship between the TyG index and NAFLD. Thus, we investigated the relationship between the TyG index and NAFLD and the effectiveness of the TyG index compared with the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) in identifying NAFLD in Korean adults.
Methods Participants of 4,986 who underwent ultrasonography in a health promotion center were enrolled. The TyG index was calculated as ln [fasting triglycerides (mg/dL)×fasting glucose (mg/dL)/2], and HOMA-IR was estimated. NAFLD was diagnosed by ultrasonography.
Results Significant differences were observed in metabolic parameters among the quartiles of the TyG index. The prevalence of NAFLD significantly increased with increment in the TyG index. After adjusting for multiple risk factors, a logistic regression analysis was performed. When the highest and lowest quartiles of the TyG index and HOMA-IR were compared, the odds ratios for the prevalence of NAFLD were 2.94 and 1.93 (95% confidence interval, 2.32 to 3.72 and 1.43 to 2.61; both
P for trend <0.01), respectively. According to the receiver operating characteristic analysis, the TyG index was superior to HOMA-IR in predicting NAFLD.Conclusion The TyG index and prevalence of NAFLD were significantly related and the TyG index was superior to HOMA-IR in predicting NAFLD in Korean adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Triglyceride-glucose body mass index predicts prognosis in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction
Ming Liu, Jianyuan Pan, Ke Meng, Yuwei Wang, Xueqing Sun, Likun Ma, Xiaofan Yu
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index is capable of identifying metabolically obese, normal-weight older individuals
Bokun Kim, Keisuke Taniguchi, Tomonori Isobe, Sechang Oh
Journal of Physiological Anthropology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of triglyceride/glucose index and related parameters with Indian Diabetes Risk Score assessment in non-diabetic individuals visiting primary healthcare centre—A community-based cross-sectional study
Sivapragasam Ramalingam, Amlan Kumar Kar, Rajini Senthil
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2024; 13(1): 235. CrossRef - Insulin resistance in NSCLC: unraveling the link between development, diagnosis, and treatment
Shizhang Zhan, Liu Wang, Wenping Wang, Ruoran Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between the triglyceride–glucose index and prognosis in postoperative renal cell carcinoma patients: a retrospective cohort study
Guoliang Qin, Zhuang Sun, Yuxiang Jin, Xiangguo Ren, Zhaocun Zhang, Shuo Wang, Guanwen Zhou, Kun Huang, Haifeng Zhao, Xianzhou Jiang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Profiling triglyceride-glucose index in Filipinos with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a single-center study
Chastene Christopher Flake, Madonna Morales-Valenzuela, Raphael Enrique Tiongco, Annalyn Navarro
The Egyptian Journal of Internal Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Performance of Insulin Resistance Indices for Identifying Metabolic Dysfunction–Associated Fatty Liver Disease
A. Lum Han, Hee Kyung Lee, Sae Ron Shin
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Triglyceride-Glucose Index is Associated with Vitamin D Status in Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease
Zhiping Liu, Wensha Zhang, Zhiwei Zhao, Wenhao Li, Jinhua Zhang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 2651. CrossRef - The triglyceride and glucose index and risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A dose–response meta-analysis
Qin Ling, Jiawei Chen, Xiao Liu, Yi Xu, Jianyong Ma, Peng Yu, Kai Zheng, Fuwei Liu, Jun Luo
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride–Glucose Index as a Potential Indicator of Sarcopenic Obesity in Older People
Bokun Kim, Gwonmin Kim, Yongkook Lee, Keisuke Taniguchi, Tomonori Isobe, Sechang Oh
Nutrients.2023; 15(3): 555. CrossRef - Association of insulin resistance with bone mineral density in a nationwide health check-up population in China
Ming Zhuo, Ze Chen, Mao-Lin Zhong, Fang Lei, Juan-Juan Qin, Shuhua Liu, Ye-Mao Liu, Tao Sun, Xiao-Jing Zhang, Lihua Zhu, Jingjing Cai, Jun-Ming Ye, Erping Yang
Bone.2023; 170: 116703. CrossRef - Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Mortality: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 220. CrossRef - Comparison of the prognostic value of a comprehensive set of predictors in identifying risk of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease among employed adults
Ze Yang, Bin Yu, Zihang Wang, Zhitao Li, Bo Yang, Honglian Zeng, Shujuan Yang
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The triglyceride glucose index and CDKAL1 gene rs10946398 SNP are associated with NAFLD in Chinese adults
Jun ZHU, Dujuan XU, Ruihua YANG, Min LIU, Ying LIU
Minerva Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - PNPLA3 rs738409 risk genotype decouples TyG index from HOMA2-IR and intrahepatic lipid content
Ákos Nádasdi, Viktor Gál, Tamás Masszi, Anikó Somogyi, Gábor Firneisz
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Baseline level and change trajectory of the triglyceride-glucose index in relation to the development of NAFLD: a large population-based cohort study
Yaqin Wang, Jiangang Wang, Lei Liu, Pingting Yang, Shuwen Deng, Xuelian Liu, Linlin Zhao, Changfa Wang, Ying Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing temporal differences in the predictive power of baseline TyG-related parameters for future diabetes: an analysis using time-dependent receiver operating characteristics
Maobin Kuang, Ruijuan Yang, Xin Huang, Chao Wang, Guotai Sheng, Guobo Xie, Yang Zou
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic Score for Insulin Resistance (METS-IR) Predicts Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Ischemic Cardiomyopathy
Xuehe Zhang, Fen Liu, Wenling Li, Jixin Zhang, Tong Zhang, Xiaolin Yu, Junyi Luo, Qian Zhao, Jinyu Zhang, Binbin Fang, Yining Yang, Xiaomei Li
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 1283. CrossRef - Prevalence and Risk Factors of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Among Hospital Staff
Daya Zhang, Lijun Zhang, Shiju Chen, Runxiang Chen, Xiaodong Zhang, Feihu Bai
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 1221. CrossRef - The metabolic score of insulin resistance is positively correlated with bone mineral density in postmenopausal patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Peng Gu, Bin Pu, Qiao Xin, Dan Yue, LieLiang Luo, JiaSheng Tao, HaiShan Li, Ming Chen, MingHua Hu, XiaoRong Hu, XiaoHui Zheng, ZhanPeng Zeng
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence estimates of the insulin resistance and associated prevalence of heart failure among United Status adults
Xiaozhong Li, Jihong Wang, Liyan Niu, Ziqi Tan, Jianyong Ma, Ling He, Peng Yu, Xiao Liu, Juxiang Li
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - From NAFLD to HCC: Advances in noninvasive diagnosis
Qinchen Xu, Maoxiao Feng, Yidan Ren, Xiaoyan Liu, Huiru Gao, Zigan Li, Xin Su, Qin Wang, Yunshan Wang
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 165: 115028. CrossRef - Usefulness of two-dimensional shear wave elastography in the assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents
Jong Seo Yoon, Kyoung Ja Lim, Il Tae Hwang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A non-linear relationship between triglyceride glucose waist circumference and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a Japanese population: a secondary analysis
Xiaojie He, Xinyue Huang, Yafang Qian, Ting Sun
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Neck Circumference as a Predictor of Insulin Resistance in People with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Da-Hye Son, Jee Hye Han, Jun-Hyuk Lee
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(3): 214. CrossRef - Prediction and Validation of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Using Insulin Resistance-Related Indices in the Japanese Population
Kengo Moriyama, Nagamu Inoue, Jin Imai, Yumi Masuda, Chizumi Yamada, Noriaki Kishimoto, Shinji Takashimizu, Akira Kubo, Yasuhiro Nishizaki
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2023; 21(9): 489. CrossRef - Application value of triglyceride-glucose index and triglyceride-glucose body mass index in evaluating the degree of hepatic steatosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Mengyuan Wang, Mingxing Chang, Peipu Shen, Wei Wei, Huayao Li, Guifang Shen
Lipids in Health and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance as a Potential Screening Test for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Korean Adults without Diabetes
Hyejung Lee, Jae-Ho Lee
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2023; 13(4): 233. CrossRef - Comparison of the Triglyceride Glucose Index and Modified Triglyceride Glucose Indices to Predict Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Youths
Kyungchul Song, Goeun Park, Hye Sun Lee, Myeongseob Lee, Hae In Lee, Han Saem Choi, Junghwan Suh, Ahreum Kwon, Ho-Seong Kim, Hyun Wook Chae
The Journal of Pediatrics.2022; 242: 79. CrossRef - The triglyceride-glucose index as a clinical useful marker for metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD): a population-based study among Iranian adults
Ehsaneh Taheri, Mohammad Amin Pourhoseingholi, Alireza Moslem, Amir Hossein Hassani, Alireza Mousavi Jarrahi, Hamid Asadzadeh Aghdaei, Mohammad Reza Zali, Behzad Hatami
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2022; 21(1): 97. CrossRef - Comparison of triglyceride-glucose index and HOMA-IR for predicting prevalence and incidence of metabolic syndrome
Da-Hye Son, Hye Sun Lee, Yong-Jae Lee, Jun-Hyuk Lee, Jee-Hye Han
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2022; 32(3): 596. CrossRef - Triglycerides/Glucose Index Is Associated with Sperm Parameters and Sperm DNA Fragmentation in Primary Infertile Men: A Cross-Sectional Study
Federico Belladelli, Luca Boeri, Edoardo Pozzi, Giuseppe Fallara, Christian Corsini, Luigi Candela, Walter Cazzaniga, Daniele Cignoli, Luca Pagliardini, Alessia D’Arma, Paolo Capogrosso, Eugenio Ventimiglia, Francesco Montorsi, Andrea Salonia
Metabolites.2022; 12(2): 143. CrossRef - Association of triglyceride-glucose index and stroke recurrence among nondiabetic patients with acute ischemic stroke
Xiaomeng Yang, Guangyao Wang, Jing Jing, Anxin Wang, Xiaoli Zhang, Qian Jia, Xia Meng, Xingquan Zhao, Liping Liu, Hao Li, Yongjun Wang, Yilong Wang
BMC Neurology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The triglycerides and glucose (TyG) index: A new marker associated with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in obese patients
Benjamin Rivière, Audrey Jaussent, Valérie Macioce, Stéphanie Faure, Nicolas Builles, Patrick Lefebvre, Philippe Géraud, Marie-Christine Picot, Sandra Rebuffat, Eric Renard, Valérie Paradis, Marie-Dominique Servais, Nathalie de Preville, David Nocca, Anne
Diabetes & Metabolism.2022; 48(4): 101345. CrossRef - Association of triglyceride-glucose with cardiac hemodynamics in type 2 diabetes
Chenxi Wang, Zhicong Zhao, Xia Deng, Zhensheng Cai, Tian Gu, Lian Li, Chang Guo, Dong Wang, Ling Yang, Li Zhao, Guoyue Yuan
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2022; 19(2): 147916412210833. CrossRef - Comparison of the Modified TyG Indices and Other Parameters to Predict Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Youth
Kyungchul Song, Hae Won Lee, Han Saem Choi, Goeun Park, Hye Sun Lee, Su Jin Kim, Myeongseob Lee, Junghwan Suh, Ahreum Kwon, Ho-Seong Kim, Hyun Wook Chae
Biology.2022; 11(5): 685. CrossRef - Triglyceride-Glucose Index for Early Prediction of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis of 121,975 Individuals
Azizullah Beran, Hazem Ayesh, Mohammed Mhanna, Waseem Wahood, Sami Ghazaleh, Ziad Abuhelwa, Wasef Sayeh, Nameer Aladamat, Rami Musallam, Reem Matar, Saif-Eddin Malhas, Ragheb Assaly
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(9): 2666. CrossRef - Triglyceride and Glucose Index as a Screening Tool for Nonalcoholic Liver Disease in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
Anca Maria Amzolini, Mircea-Cătălin Forțofoiu, Anca Barău Alhija, Ionela Mihaela Vladu, Diana Clenciu, Adina Mitrea, Maria Forțofoiu, Daniela Matei, Magdalena Diaconu, Marinela Sinziana Tudor, Elena Simona Micu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(11): 3043. CrossRef - Triglyceride glucose index is superior biomarker for predicting type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents
Jong Seo Yoon, Hye Jin Lee, Hwal Rim Jeong, Young Suk Shim, Min Jae Kang, Il Tae Hwang
Endocrine Journal.2022; 69(5): 559. CrossRef - Triglyceride and glucose index is a simple and easy‐to‐calculate marker associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Kyung‐Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong‐Yup Ahn, Cheol‐Young Park
Obesity.2022; 30(6): 1279. CrossRef - Evaluating Triglyceride and Glucose Index as a Simple and Easy-to-Calculate Marker for All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, You-Cheol Hwang, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of General Internal Medicine.2022; 37(16): 4153. CrossRef - The Role of Insulin Resistance in Fueling NAFLD Pathogenesis: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Implications
Rossella Palma, Annamaria Pronio, Mario Romeo, Flavia Scognamiglio, Lorenzo Ventriglia, Vittorio Maria Ormando, Antonietta Lamazza, Stefano Pontone, Alessandro Federico, Marcello Dallio
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(13): 3649. CrossRef - Comparison of the diagnostic value between triglyceride-glucose index and triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease patients: a retrospective cross-sectional study
Zhi Liu, He He, Yuzhao Dai, Lidan Yang, Shenling Liao, Zhenmei An, Shuangqing Li
Lipids in Health and Disease.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin Resistance Markers to Detect Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Male Hispanic Population
Maritza Pérez-Mayorga, Jose P. Lopez-Lopez, Maria A. Chacon-Manosalva, Maria G Castillo, Johanna Otero, Daniel Martinez-Bello, Diego Gomez-Arbelaez, Daniel D. Cohen, Patricio Lopez-Jaramillo, Federico Ravaioli
Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Risk factors and prediction model for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in northwest China
Danting Li, Meiyu Zhang, Shengli Wu, Huiwen Tan, Nong Li
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The triglyceride glucose index is associated with the cerebral small vessel disease in a memory clinic population
Jiayu Zhang, Ming Hu, Yanqiu Jia, Shicong Zhao, Peiyuan Lv, Mingyue Fan, Yuanyuan Shi, Wei Jin
Journal of Clinical Neuroscience.2022; 104: 126. CrossRef - Integrating experimental model, LC-MS/MS chemical analysis, and systems biology approach to investigate the possible antidiabetic effect and mechanisms of Matricaria aurea (Golden Chamomile) in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yassin Ismail, Dina M. Fahmy, Maivel H. Ghattas, Mai M. Ahmed, Walaa Zehry, Samy M. Saleh, Dina M. Abo-elmatty
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Laboratory data clustering in defining population cohorts: Case study on metabolic indicators
Ivan Pavicevic, Goran Miljus, Olgica Nedic
Journal of the Serbian Chemical Society.2022; 87(9): 1025. CrossRef - Association of triglyceride glucose-body mass index with non-small cell lung cancer risk: A case-control study on Chinese adults
Feifei Wang, Ting He, Guoliang Wang, Tuo Han, Zhongqiang Yao
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Risk of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Cohort Study
Ru Zhang, Qing Guan, Mengting Zhang, Yajie Ding, Zongzhe Tang, Hongliang Wang, Wei Zhang, Yue Chen, Rong Jiang, Yan Cui, Jie Wang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 3167. CrossRef - Association between the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index and increased blood pressure in normotensive subjects: a population-based study
Dong-Hwa Lee, Jong Eun Park, So Young Kim, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Jong-Hyock Park
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Fructose consumption correlates with triglyceride-glucose index and glycemic status in healthy adults
Eda Keskin, Havvanur Yoldas Ilktac
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN.2022; 52: 184. CrossRef - Associations Between Type 2 Diabetes Subtypes and Complications: Analysis of the Malaysia National Diabetes Registry
Rasa Kazlauskaite, Nathan Ellermeier, Carrie Ngongo, Arunah Chandran, Pankaja Desai, Ethan Ritz, Rachel Nugent, Feisul Idzwan Mustapha
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Independent and combined effects of triglyceride-glucose index on prehypertension risk: a cross-sectional survey in China
Hong Xie, Jian Song, Liangliang Sun, Xinxin Xie, Yehuan Sun
Journal of Human Hypertension.2021; 35(3): 207. CrossRef - Association of Triglyceride-Glucose Index with Bone Mineral Density in Non-diabetic Koreans: KNHANES 2008–2011
Jee Hee Yoon, A Ram Hong, Wonsuk Choi, Ji Yong Park, Hee Kyung Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang
Calcified Tissue International.2021; 108(2): 176. CrossRef - Triglyceride‐Glucose Index (TyG) is associated with erectile dysfunction: A cross‐sectional study
Mehmet Yilmaz, Mustafa Karaaslan, Senol Tonyali, Mecit Celik, Tuncay Toprak, Oner Odabas
Andrology.2021; 9(1): 238. CrossRef - Triglyceride Glucose Index and Related Parameters (Triglyceride Glucose-Body Mass Index and Triglyceride Glucose-Waist Circumference) Identify Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver and Liver Fibrosis in Individuals with Overweight/Obesity
Mohammad E. Khamseh, Mojtaba Malek, Rowshanak Abbasi, Hoda Taheri, Maryam Lahouti, Fariba Alaei-Shahmiri
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2021; 19(3): 167. CrossRef - Triglyceride and glucose index and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Jung A Kim, Jinsil Kim, Eun Roh, So-hyeon Hong, You-Bin Lee, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi, Eunjin Noh, Soon Young Hwang, Geum Joon Cho, Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 171: 108533. CrossRef - Association of the triglyceride and glucose index with low muscle mass: KNHANES 2008–2011
Jung A. Kim, Soon Young Hwang, Ji Hee Yu, Eun Roh, So-hyeon Hong, You-Bin Lee, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A. Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The triglycerides and glucose index is strongly associated with hepatic steatosis in children with overweight or obesity
Luis E. Simental-Mendía, César Javier Ortega-Pacheco, Elvira García-Guerrero, María Alejandra Sicsik-Aragón, Fernando Guerrero-Romero, Gerardo Martínez-Aguilar
European Journal of Pediatrics.2021; 180(6): 1755. CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index and the risk of stroke and its subtypes in the general population: an 11-year follow-up
Anxin Wang, Guangyao Wang, Qian Liu, Yingting Zuo, Shuohua Chen, Boni Tao, Xue Tian, Penglian Wang, Xia Meng, Shouling Wu, Yongjun Wang, Yilong Wang
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Triglyceride Glucose Index and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Risk in Chinese Population
Xin Yan, Yujuan Gao, Jingzhi Tong, Mi Tian, Jinghong Dai, Yi Zhuang
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride Glucose Index Is Associated With Arterial Stiffness and 10-Year Cardiovascular Disease Risk in a Chinese Population
Wen Guo, Wenfang Zhu, Juan Wu, Xiaona Li, Jing Lu, Pei Qin, Cheng Zhu, Nianzhen Xu, Qun Zhang
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - An Analysis of the Potential Relationship of Triglyceride Glucose and Body Mass Index With Stroke Prognosis
Zongyi Hou, Yuesong Pan, Yindong Yang, Xiaofan Yang, Xianglong Xiang, Yilong Wang, Zixiao Li, Xingquan Zhao, Hao Li, Xia Meng, Yongjun Wang
Frontiers in Neurology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals in the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Comprehensive Review
Raquel Cano, José Pérez, Lissé Dávila, Ángel Ortega, Yosselin Gómez, Nereida Valero-Cedeño, Heliana Parra, Alexander Manzano, Teresa Véliz Castro, María Albornoz, Gabriel Cano, Joselyn Rojas-Quintero, Maricarmen Chacín, Valmore Bermúdez
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(9): 4807. CrossRef - Triglyceride glucose (TyG) index and the progression of liver fibrosis: A cross-sectional study
Helda Tutunchi, Fatemeh Naeini, Majid Mobasseri, Alireza Ostadrahimi
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN.2021; 44: 483. CrossRef - Newly proposed insulin resistance indexes called TyG-NC and TyG-NHtR show efficacy in diagnosing the metabolic syndrome
M. Mirr, D. Skrypnik, P. Bogdański, M. Owecki
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2021; 44(12): 2831. CrossRef - Association Between the Triglyceride–Glucose Index and Outcomes of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Large-Scale Health Management Cohort Study
Jing Liu, Liying Guan, Meng Zhao, Qihang Li, An Song, Ling Gao, Haiyan Lin, Jiajun Zhao
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 2829. CrossRef - Association between triglyceride-glucose index and thyroid function in euthyroid adults: The Korea National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey 2015
Wonsuk Choi, Ji Yong Park, A. Ram Hong, Jee Hee Yoon, Hee Kyung Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sun Young Lee
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(7): e0254630. CrossRef - Triglyceride glucose-waist to height ratio: a novel and effective marker for identifying hepatic steatosis in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Mojtaba Malek, Mohammad E. Khamseh, Haleh Chehrehgosha, Sohrab Nobarani, Fariba Alaei-Shahmiri
Endocrine.2021; 74(3): 538. CrossRef - The association between triglyceride-glucose index, cardio-cerebrovascular diseases, and death in Korean adults: A retrospective study based on the NHIS-HEALS cohort
Joungyoun Kim, Sang-Jun Shin, Hee-Taik Kang, Claudio Passino
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(11): e0259212. CrossRef - A population-based study of TyG index distribution and its relationship to cardiometabolic risk factors in children and adolescents
Jong Seo Yoon, Young Suk Shim, Hae Sang Lee, Il Tae Hwang, Jin Soon Hwang
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of several blood lipid-related indexes in the screening of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in women: a cross-sectional study in the Pearl River Delta region of southern China
Jingrui Wang, Zhenzhen Su, Yijin Feng, Ruihan Xi, Jiamin Liu, Peixi Wang
BMC Gastroenterology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The value of the triglyceride-glucose index in the diagnosis of insulin resistance in early forms of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
A. A. Shipovskaya, N. A. Larina, I. V. Kurbatova, O. P. Dudanova
Experimental and Clinical Gastroenterology.2021; (10): 43. CrossRef - Triglyceride Glucose-Waist Circumference Is Superior to the Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance in Identifying Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Healthy Subjects
Hwi Seung Kim, Yun Kyung Cho, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Chang Hee Jung, Joong-Yeol Park, Hong-Kyu Kim, Woo Je Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 11(1): 41. CrossRef - Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance and lobular inflammation in nondiabetic patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: methodological considerations
Denis Monneret, Dominique Bonnefont-Rousselot
European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2020; 32(4): 542. CrossRef - Helicobacter pylori infection may increase the severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via promoting liver function damage, glycometabolism, lipid metabolism, inflammatory reaction and metabolic syndrome
Chen Chen, Caiyun Zhang, Xuelin Wang, Feijuan Zhang, Ze Zhang, Pengchai Ma, Shuzhi Feng
European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2020; 32(7): 857. CrossRef - Beneficial effect of anti-diabetic drugs for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Kyung-Soo Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2020; 26(4): 430. CrossRef - The triglyceride-glucose index is associated with the severity of hepatic steatosis and the presence of liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a cross-sectional study in Chinese adults
Wen Guo, Jing Lu, Pei Qin, Xiaona Li, Wenfang Zhu, Juan Wu, Nianzhen Xu, Qun Zhang
Lipids in Health and Disease.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between triglyceride glucose-body mass index and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in the non-obese Chinese population with normal blood lipid levels: a secondary analysis based on a prospective cohort study
Yaling Li, Rui Zheng, Jie Li, Shuyi Feng, Li Wang, Zhiming Huang
Lipids in Health and Disease.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Triglyceride-glucose body mass index predicts prognosis in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction

- Clinical Study
- Calpain-10 and Adiponectin Gene Polymorphisms in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Patients
- Ji Sun Nam, Jung Woo Han, Sang Bae Lee, Ji Hong You, Min Jin Kim, Shinae Kang, Jong Suk Park, Chul Woo Ahn
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(3):364-371. Published online September 18, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.3.364
- 3,524 View
- 50 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Genetic variations in calpain-10 and adiponectin gene are known to influence insulin secretion and resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Recently, several single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in calpain-10 and adiponectin gene have been reported to be associated with type 2 diabetes and various metabolic derangements. We investigated the associations between specific calpain-10 and adiponectin gene polymorphisms and Korean type 2 diabetes patients.
Methods Overall, 249 type 2 diabetes patients and 131 non-diabetic control subjects were enrolled in this study. All the subjects were genotyped for SNP-43 and -63 of calpain-10 gene and G276T and T45G frequencies of the adiponectin gene. The clinical characteristics and measure of glucose metabolism were compared within these genotypes.
Results Among calpain-10 polymorphisms, SNP-63 T/T were more frequent in diabetes patients, and single SNP-63 increases the susceptibility to type 2 diabetes. However, SNP-43 in calpain-10 and T45G and intron G276T in adiponectin gene were not significantly associated with diabetes, insulin resistance, nor insulin secretion.
Conclusion Variations in calpain-10, SNP-63 seems to increase the susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in Koreans while SNP-43 and adiponectin SNP-45, -276 are not associated with impaired glucose metabolism.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Decoding type 2 diabetes mellitus genetic risk variants in Pakistani Pashtun ethnic population using the nascent whole exome sequencing and MassARRAY genotyping: A case-control association study
Asif Jan, Zakiullah, Sajid Ali, Basir Muhammad, Amina Arshad, Yasar Shah, Haji Bahadur, Hamayun Khan, Fazli Khuda, Rani Akbar, Kiran Ijaz, Giuseppe Novelli
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(1): e0281070. CrossRef - Silencing LncRNA PVT1 Reverses High Glucose-Induced Regulation of the
High Expression of PVT1 in HRMECs by Targeting miR-128-3p
Xuyang Wang, Wangling Chen, Wei Lao, Yunxin Chen
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2022; 54(02): 119. CrossRef - Association of CAPN10 (SNP-19) genetic polymorphism and obesity with T2DM: a study on Bengali Hindu caste population
Pranabesh Sarkar, Diptendu Chatterjee, Arup Ratan Bandyopadhyay
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2021; 41(1): 37. CrossRef - Association of Candidate Gene Polymorphism with Metabolic Syndrome among Mongolian Subjects: A Case-Control Study
Ariunbold Chuluun-Erdene, Orgil Sengeragchaa, Tsend-Ayush Altangerel, Purevjal Sanjmyatav, Batnaran Dagdan, Solongo Battulga, Lundiamaa Enkhbat, Nyamjav Byambasuren, Munkhzol Malchinkhuu, Munkhtstetseg Janlav
Medical Sciences.2020; 8(3): 38. CrossRef - Meta-analysis of the association between adiponectin SNP 45, SNP 276, and type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yuwei Dong, Gongping Huang, Xin Wang, Zhaoming Chu, Jingzhi Miao, Houwen Zhou, Mingqing Xu
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(10): e0241078. CrossRef - Association of three SNPs in adiponectin gene with lipid traits of Tianzhu Black Muscovy (Cairina moschata)
Yuan-Yu Qin, Yi-Yu Zhang, Hua-Lun Luo, Lei Wu
Molecular Biology Reports.2019; 46(1): 325. CrossRef
- Decoding type 2 diabetes mellitus genetic risk variants in Pakistani Pashtun ethnic population using the nascent whole exome sequencing and MassARRAY genotyping: A case-control association study

- Effect of 17-beta Estradiol on Adipocyte Lipin-1 Expression in OLETF Rat.
- Eun Seok Kang, In Sook Kim, Seok Jin Ko, Chul Hoon Kim, Sung Wan Chun, Chul Woo Ahn, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2010;25(3):199-205. Published online September 1, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2010.25.3.199
- 2,006 View
- 21 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
17 beta-estradiol is known to play an important role in glucose homeostasis. Lipin-1 is a nuclear protein that is essential in adipocyte differentiation and it is considered to play a role in ectopic fat deposition and the redistribution of fat. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of 17 beta-estradiol on the lipin-1 expression in the adipocytes of OLETF rats, which is an animal model of diabetes. METHODS: The OLETF rats were divided into 3 groups, 1) the sham-operation group (SHAM) 2) the castrated group (CAST) and 2) the castrated and estradiol treatment group (EST), and all the rats were at 6 weeks of age. LETO rats were used as a control group (LETO). 0.1 mg of estradiol valerate was injected subcutaneously every 4 weeks in the rats of the EST group. The visceral and subcutaneous tissues were isolated to evaluate the lipin-1 protein expression. The lipin-1 expression was measured in human visceral and subcutaneous preadipocytes. RESULTS: Less body weight gain was observed in the EST group compared with that of the SHAM group. In addition, improvement in the glucose tolerance was observed in the EST group. The lipin-1 expression in visceral fat was decreased in the SHAM and CAST groups, but it was but recovered in the EST group. The lipin-1 expression in the subcutaneous fat was decreased in the SHAM, CAST, and EST groups. CONCLUSION: Long term estradiol treatment in OLETF rats reduces the body weight gain and improves the glucose tolerance. Estradiol enhances the lipin-1 protein expression in the visceral adipocytes, but not in the subcutaneous adipocytes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of 17-beta Estradiol on Adipocyte Lipin-1 Expression in OLETF Rat
Seong-Kyu Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2010; 25(3): 177. CrossRef
- Effect of 17-beta Estradiol on Adipocyte Lipin-1 Expression in OLETF Rat

- Retraction: Expression of RET in Thyroid Diseases of a Korean Population.
- Si Hoon Lee, Soon Won Hong, Woo Chul Moon, Myoung Ryur Oh, Jin Kyung Lee, Bong Soo Cha, Chul Woo Ahn, Kyung Rae Kim, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008;23(1):70. Published online February 1, 2008
- 1,118 View
- 16 Download

- Retraction: Contributing Factors to Different Natural Courses of Posttansplantation Diabetes Mellitus in Renal Allograft Recipients.
- Kyu Yeon Hur, Myoung Soo Kim, Jae Hyun Nam, Eun Seok Kang, Hyun Joo Lee, So Hun Kim, Bong Soo Cha, Chul Woo Ahn, Soon Il Kim, Yu Seun Kim, Hyun Chul Lee
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2007;22(6):479. Published online December 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2007.22.6.479
- 1,520 View
- 21 Download

- A Case of Turner's Syndrome with Transient Hypopituitarism.
- Ji Sun Nam, Min Ho Cho, Jung Min Roh, Hai Jin Kim, Ji Eun Yoon, Han Young Jung, Jong Suk Park, Eun Seok Kang, Chul Woo Ahn, Bong Soo Cha, Eun Jig Lee, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2007;22(4):266-271. Published online August 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2007.22.4.266
- 1,715 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Turner's syndrome is characterized by short stature and gonadal dysgenesis, and it is often associated with various systemic manifestations, such as cardiovascular, renal, thyroidal, gastrointestinal, and musculoskeletal disorders. Though very rare, it can also be accompanied by hypopituitarism. It is important to give a meticulous medical attention to short females with gonadal dysgenesis so that neither disease is neglected or gets delayed diagnosis. In this case, Turner's syndrome and hypopituitarism were diagnosed almost simultaneously, but hypopiuitarism was transient, and the normal pituitary function was recovered spontaneously without any treatment. Initial sella MRI showed mild congenital hypoplastic hypopituitarism, and combined pituitary function test was compatible with hypopituitarism, but after 5 years, though growth hormone deficiency was still present, otherwise normal pituitary function was noted without any change in MRI. Herein, we are reporting a case of Turner's syndrome with transient idiopathic hypopituitarism with the review of literature.

- A Case of Autoimmune Hypoglycemia due to Insulin Antibody in Patient with End Stage Renal Disease.
- Ji Ye Jung, Eun Seok Kang, Beom Seok Kim, Sung Wan Chun, Yumie Rhee, Chul Woo Ahn, Bong Soo Cha, Eun Jig Lee, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(6):536-541. Published online December 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.6.536
- 1,636 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fasting hypoglycemia results from several mechanisms. Autoimmune hypoglycemia is one of the rare causes of hypoglycemia, and characterized by hyperinsulinemia, fasting hypoglycemia and the presence of autoantibodies to insulin or insulin receptor. We report here on a 64-year-old male patient with autoimmune hypoglycemia with end stage renal disease. He had no history of diabetes or insulin use. He had experienced several severe hypoglycemic events. The serum C-peptide level was 7.48 ng/mL and the insulin concentration was 115.4 micro U/mL when the fasting plasma glucose level was 88 mg/dL. The insulin to glucose ratio was 5.42, which suggested the presence of insulinoma. Yet the radiologic studies, including magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography, endoscopic ultrasonography and selective calcium stimulated venous sampling revealed no evidence of insulinoma. The insulin autoantibody level was 62 micro U/mL. Therefore, we could diagnosis the autoimmune hypoglycemia. The hypoglycemia was treated with prednisolone and the patient recovered from this. His insulin level decreased to 21.11 micro U/mL and the insulin autoantibody level decreased to 34 micro U/mL. Hypoglycemia in the hemodialysis patients is not uncommon. One should bear in mind autoimmune hypoglycemia as one of the causes of hypoglycemia in patients with no history of diabetes.

- Contributing Factors to Different Natural Courses of Posttansplantation Diabetes Mellitus in Renal Allograft Recipients.
- Kyu Yeon Hur, Myoung Soo Kim, Jae Hyun Nam, Eun Seok Kang, Hyun Joo Lee, So Hun Kim, Bong Soo Cha, Chul Woo Ahn, Soon Il Kim, Yu Seun Kim, Hyun Chul Lee
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(5):373-381. Published online October 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.5.373
- 1,994 View
- 22 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
New onset diabetes is a major complication after kidney transplantation. However, the natural course of posttransplantation diabetes mellitus (PTDM) remains unclear. The aim of this study was to demonstrate the detailed natural courses of PTDM according to the onset and persistency of hyperglycemia, and to investigate risk factors for development of different courses of PTDM in renal allograft recipients. METHODS: A total of 77 renal allograft recipients without previously known diabetes were enrolled and performed a serial 75 g oral glucose tolerance test at 0, 1, and 7 years after kidney transplantation. Patients were classified according to the onset and persistency of PTDM: early PTMD (E-PTDM), late PTDM (L-PTDM), persistent PTDM (P-PTDM), transient PTMD (T-PTDM), and non-PTDN (N-PTDM). RESULTS: The incidence of each group was as follows: E-PTDM, 39%; L-PTDM, 11.7%; P-PTDM, 23.4% T-PTDM, 15.6%; N-PTDM, 49.3%. Tacrolimus and female gender were associated with the development of E-PTDM. Among E-PTDM, age at transplantation was a high risk factor for the development of P-PTDM. Higher BMI at year1 was associated with the development of L-PTDM. CONCLUSION: Different risk factors were associated with various natural courses of PTDM. Since old age and female gender are not modifiable risk factors, it may be important to modify immunosuppressive therapy regimens for the prevention of E-PTDM and control of body weight for L-PTDM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and Safety of Gemigliptin in Post-Transplant Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Jaehyun Bae, Youjin Kim, Yongin Cho, Minyoung Lee, Ji-Yeon Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Dong Jin Joo, Kyu Ha Huh, Myoung Soo Kim, Yu Seun Kim, Eun Seok Kang
Transplantation Proceedings.2019; 51(10): 3444. CrossRef - Post-transplantation Diabetes Mellitus
Kun-Ho Yoon
Journal of Korean Endocrine Society.2006; 21(5): 370. CrossRef
- Efficacy and Safety of Gemigliptin in Post-Transplant Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus

- The Relationship between the Leptin Concentration and the Small Dense Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Concentration in Korean Type 2 Diabetic Patients.
- Wan Sub Shim, Hae Jin Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Yu Mie Rhee, Chul Woo Ahn, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee, Bong Soo Cha
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(4):319-327. Published online August 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.4.319
- 1,833 View
- 20 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Leptin has been suggested as a possible cause of atherosclerotic disease. The small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) has also been regarded as a new surrogate marker in atherosclerotic disease. The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationship between the leptin concentration and the small dense LDL-C concentration in Korean type 2 diabetic patients. METHODS: One hundred-ninety one type 2 diabetic patients, who did not use any medication that could affect the concentration of lipid such as statin, fibrate, thiazolidinediones and corticosteroid, were enrolled in this study. We analyzed the relationship between leptin, the small dense LDL-C and the other metabolic parameters. RESULTS: The small dense LDL-C concentrations were higher in the group with the highest tertile of the leptin value, both in males and females than those patients in the group with the lowest tertile of the leptin value. The small dense LDL-C concentrations were also higher in the group with the highest tertile of leptin divided by the BMI value both in males and females than those patients in the group with the lowest tertile of the leptin value. The leptin concentration was positively correlated with the small dense LDL-C, total cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL-C, insulin and HOMAIR values after adjusting for age, gender and BMI. CONCLUSION: The association between leptin and small dense LDL-C could be a factor that explains the association between leptin and cardiovascular disease. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationships among Serum Adiponectin, Leptin and Vitamin D Concentrations and the Metabolic Syndrome in Farmers
Seo-Eun Yeon, Hee-Ryoung Son, Jung-Sook Choi, Eun-Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(1): 12. CrossRef - The Effect of Visceral Fat Area and Adipocytokines on Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Case-Control Study in Adult Korean Population
Kang-Kon Lee, Young-Sung Suh, Keun-Sang Yum
The Korean Journal of Obesity.2012; 21(1): 57. CrossRef
- Relationships among Serum Adiponectin, Leptin and Vitamin D Concentrations and the Metabolic Syndrome in Farmers

- A Case of Patient with Opioid-Induced Adrenocortical Insufficiency and Hypogonadism.
- Hai Jin Kim, Chul Sik Kim, Jong Suk Park, Jina Park, Eun Seok Kang, Chul Woo Ahn, Bong Soo Cha, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(3):257-260. Published online June 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.3.257
- 1,810 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Opioids are known to decrease plasma cortisol and testosterone level in human and other mammals. Nowadays, opioid use is exponentially increasing, but little is known about its side effects. With the help of progressive human science, we can habit longer life and as result, are becoming more avid for healthy life. In this respect, analgesics play important role in maintaining good and healthy quality of life. For this reason, it is important to fully understand its side effects and handle it with special precaution. We are reporting a 22-year-old male who had been taken opioid analgesic for more than six years to relieve chronic, intractable headache. Then, his hormone test revealed hypogonadotropic hypogonadism combined with hypoadrenocorticotropic hypoadrenalism but showed no definite clinical features except for sexual frigidity. After two years of oxycodon discontinuation, we reevaluated that his hormone test, and all other laboratory tests returned to the normal range.

- Reversible Pituitary Dysfunction in a Patient with Cushing's Syndrome due to Adrenal Adenoma.
- Jee Hyun Kong, Kyung Wook Kim, Hei Jin Kim, Ji Sun Nam, Jin A Park, Jong Sook Park, Chul Sik Kim, Byung Soo Moon, Soon Won Hong, Chul Woo Ahn, Kyung Rae Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(2):146-152. Published online April 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.2.146
- 1,620 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 45-year-old woman who complained of weight gain and irregular menstruation was diagnosed as having Cushing's syndrome due to a 3 cm sized left adrenal adenoma. She underwent left adrenalectomy, and she also underwent combined anterior pituitary tests before and 9 months after the surgery. The growth hormone and adrenocorticotropic hormone levels failed to respond to hypoglycemia before the surgery, but their responses recovered after the surgery. Cortisol and thyroid stimulating hormone failed to respond to hypoglycemia and thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) before the surgery, respectively, but these were improved after the surgery. Luteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone, and prolactin adequately responded to gonadotropin-releasing hormone and TRH, respectively, before and after the surgery. However, the basal levels of these hormones were higher after adrenalectomy, suggesting that hypercortisolemia had a significant influence on all the pituitary hormones.

- A Case of Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1 with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma.
- Hai Jin Kim, Chul Sik Kim, Hyun Chul Je, Jina Park, Jong Suk Park, Jee Hyun Kong, Eun Seok Kang, Chul Woo Ahn, Bong Soo Cha, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee, Hang Suk Jang, Soon Won Hong
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(1):79-84. Published online February 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.1.79
- 1,797 View
- 21 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This is the first report of papillary thyroid carcinoma combined with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN 1). It is an hereditary syndrome characterized by neoplastic disorders such as pituitary adenoma, parathyroid adenoma or hyperplasia and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor, such as gastrinoma just like in our case. But sometimes pheochromocytoma, mucosal ganglioneuromas, lipoma, forgut carcinoid and thyroid disease could be accompany the disease, but coincidental papillary thyroid carcinoma was never reported before in Korea. Herein we represent a 39-year-old woman who manifested typical features of MEN 1 with coincidental papillary thyroid carcinoma. Despite with definite family history of MEN 1, her genetic analysis of DNA had not found any germline mutation in MEN 1 gene. Unidentified culprit gene unable further genetic study of finding LOH (loss of heterogeneity) in 11q13, the possible explanation of papillary thyroid carcinoma as a new component of MEN 1. As we have experienced a case of MEN 1 combined with papillary thyroid carcinoma, we report it with the review of literature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Case of Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type I with Atypical Clinical Course
Yun Sun Choi, Youn Sun Bai, Bon Jeong Ku, Young Suk Jo, Young Kun Kim, Heung Kyu Ro, Minho Shong
Journal of Korean Endocrine Society.2008; 23(4): 266. CrossRef
- A Case of Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type I with Atypical Clinical Course

- A Case of Acromegaly Caused by Double Pituitary Adenomas.
- Hai Jin Kim, Chul Sik Kim, Jong Suk Park, Jina Park, Jee Hyun Kong, Ji Sun Nam, Chul Woo Ahn, Bong Soo Cha, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee, Soon Won Hong
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(1):53-57. Published online February 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.1.53
- 1,958 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Acromegaly is a clinical syndrome, which is caused by an excess of growth hormone (GH), most commonly secreted from a pituitary solitary adenoma. However, our patient had bilateral GH-secreting pituitary tumors, the incidence of which has been reported in only 1.3 to 1.69% of all acromegalic patients. A 59-year-old female, with no family history of pituitary adenomas, demonstrated an increased level of serum insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), and GH not suppressed after 75 g oral glucose loading. On a preoperative MRI, only one pituitary tumor, measuring 1.1 x 0.7 cm, could be observed using sellar MRI. After surgical resection of the tumor, her headache and myalgia were sustained, and the IGF-1 level was still in a high titer. Therefore, a follow-up sellar MRI was taken, and a 0.6 x 0.7 cm sized newly growing pituitary tumor was found on the other side. With a retrospective review of radiological examinations, the patient was found to have bilateral tumors. The 0.3 cm sized tumor on the left was too small to be detected on the preoperative MRI. As the patient preferred medical treatment after surgery, she was treated with sandostatin analogues. Acromegaly with bilateral GH-secreting pituitary tumors, is a very rare disease, with no previous case having been reported in Korea. Herein, we report the case with a review of the literature.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



